Troubleshooting ESXi connectivity to iSCSI arrays using software initiators
Article ID: 311055
Updated On:
Products
VMware vSphere ESXi
Issue/Introduction
This article guides you through the most common steps to identify a connectivity problem from an ESXi host to an iSCSI shared storage device using the software initiator.
For information on troubleshooting LUN connectivity, see Troubleshooting LUN connectivity issues on ESXi hosts.
Symptoms:
- Datastores are not visible through the VMware vSphere Client or the vSphere Web Client.
- One ESXi host cannot see any targets from all storage arrays.
- The array does not report the HBA of the ESXi host as being logged in.
- The array cannot ping the software initiator on the ESXi host.
- The ESXi host cannot ping the storage processor on the array.
- The ESXi host cannot vmkping the storage processor on the array.
- The initiator does not have any logged-in initiator path unity.
- The host does not have any initiators logged into the storage system.
Environment
VMware vSphere ESXi 6.0
VMware vSphere ESXi 7.0.0
VMware vSphere ESXi 6.7
VMware vSphere ESXi 5.5
VMware vSphere ESXi 8.0.x
VMware vSphere ESXi 6.5
VMware vSphere ESXi 5.1
VMware vSphere ESXi 7.0.0
VMware vSphere ESXi 6.7
VMware vSphere ESXi 5.5
VMware vSphere ESXi 8.0.x
VMware vSphere ESXi 6.5
VMware vSphere ESXi 5.1
Resolution
VMware recommends validating that each troubleshooting step below is true for your environment. Each step will provide instructions or a link to a document, in order to eliminate possible causes and take corrective action as necessary. The steps are ordered in the most appropriate sequence to isolate the issue and identify the proper resolution. Please do not skip a step.
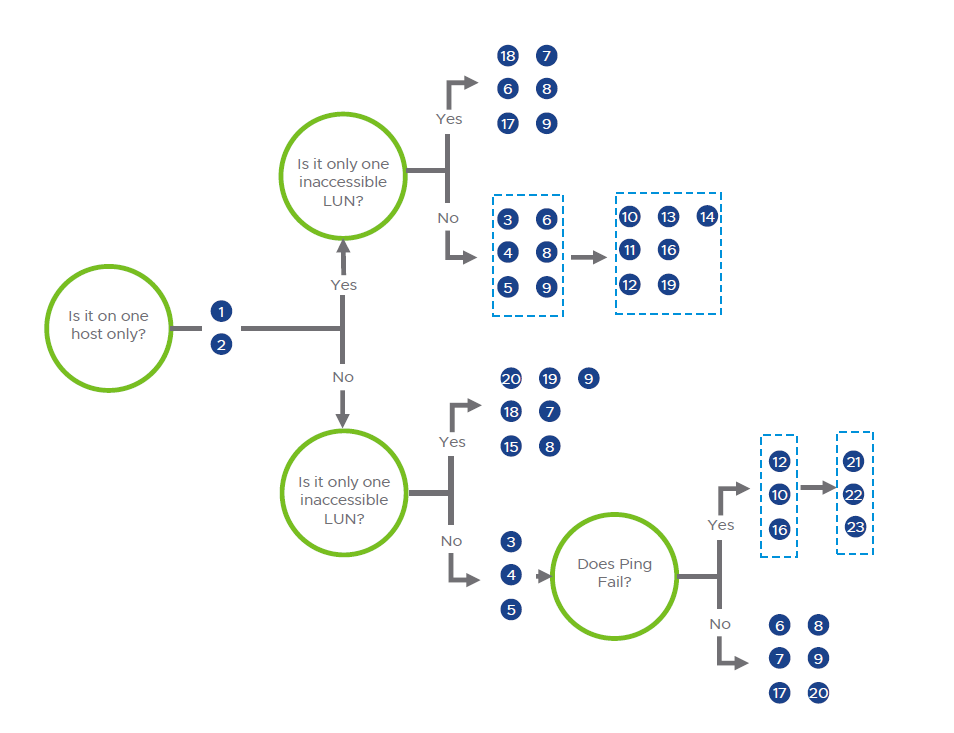
Note: The flow chart above is based on experience and logical thinking, other troubleshooting steps could be done in different scenarios.
Additional considerations:
Software iSCSI LUN Inaccessibility
Troubleshooting Flowchart
| Steps | Troubleshooting Steps |
| Rescan the Storage on the cluster level | |
| Check the driver/firmware compatibility (HCL) | |
| Check network connectivity: vmkping I < SW iSCSI vmkernel > Target_IP | |
| Check MTU size consistency using vmkping -S option | |
| Check SW iSCSI port: nc z < Target_IP > 3260 | |
| Check if the vmhba iqn exists in the initiator group from the storage side | |
| Un-present the LUN from the storage side and present it again | |
| Restart storageRM service | |
| Reboot the Host | |
| Check the iSCSI configuration according to Considerations for using software iSCSI port binding in ESX/ESXi. | |
| Recreate the vmkernel associated with SW iSCSI | |
| Remove the target and re-add it again | |
| Break the multipathing and use only one NIC to check for hardware failures | |
| Disable the SW iSCSI vmhba, reboot the host, and re-enable it again. | |
| Check the Authentication method with the storage if configured | |
| Check the presence of the target MAC address in the ARP table: esxcli network ip neighbor list | |
| Check if the LUN is appearing as a snapshot LUN: esxcfg-volume -l | |
| Check the paths state to the device: esxcfg-mpath -b -d < device-ID> | |
| Change the used VMware Multipathing policies in ESXi/ESX and if fixed is used changed the preferred path | |
| Check from the storage side if other LUNs related to the same storage group are accessible or not and try to create a new LUN and present it to the host for testing | |
| Configuring VLAN on a vSwitch standard portgroup check on the physical switch | |
| Restart physical switch | |
| Restart array controller |
Note: The flow chart above is based on experience and logical thinking, other troubleshooting steps could be done in different scenarios.
Additional considerations:
- Some arrays are using virtual IP replacing the real IPs of the array controller, so try to replace it with the real IP.
- Despite the LUN can be accessible, MTU mismatch can affect datastore creation on it.
- Verify that the storage array is listed in the VMware Hardware Compatibility Guide and that the initiator is registered on the array. Consult your storage vendor for instructions on this procedure.
- Verify that the array is configured correctly for use with your ESXi hosts. Partner with your hardware vendor to ensure that the array is properly configured. For more information, see the iSCSI SAN Configuration Guide.
- Verify that the physical hardware and physical network hardware are functioning correctly. You may have to contact your hardware vendor for information on verifying that your hardware functions correctly.
Additional Information
- Verify that the virtual switch being used for storage has been configured correctly. For more information, Best Practices for Configuring Networking with Software iSCSI section of the vSphere Storage Guide.
Note: A misconfigured jumbo frame on the iSCSI Network may delay the booting of the ESXi host which can lead to longer wait times while doing a rescan on the iSCSI LUNs. Also, Ensure that there are enough available ports on the virtual switch. For more information, see No network connectivity if all ports are in use (1009103).
- Log in to the ESXi host and verify that the host can vmkping the iSCSI targets with the command:
vmkping target_ip
Note: Ensure that the mapped iSCSI initiator name on the SAN array exactly matches (including upper and lower case) the name listed in the properties of the iSCSI initiator on the ESXi host to avoid any connectivity issues. If you have jumbo frames configured on the iSCSI network, ensure that you do the testing with the vmkping command. For help on using the vmkping command, run the command vmkping -h.
- If you are running on an ESXi host, check that you are able to
pingthe iSCSI target:
ping target_ip
For more information, see Testing network connectivity with the ping command and Testing VMkernel network connectivity with the vmkping command.
For more information, see Testing network connectivity with the ping command and Testing VMkernel network connectivity with the vmkping command.
- Use
netcat(nc) to verify whether you can reach the iSCSI TCP port (default 3260) on the storage array from the host. For example:
nc -z 10.1.10.100 3260
Connection to 10.1.10.100 3260 port [tcp/http] succeeded!
Connection to 10.1.10.100 3260 port [tcp/http] succeeded!
- VMware Skyline Health Diagnostics for vSphere - FAQ
- "An error occurred while consolidating disks" when deleting one or more snapshots or consolidate disks
Feedback
Yes
No
