Virtual machine becomes unresponsive or inactive when taking memory snapshot
Article ID: 321376
Updated On:
Products
VMware vSphere ESXi
Issue/Introduction
Symptoms:
While taking a snapshot of a virtual machine with memory, you may experience these symptoms while the memory is being written to disk:
While taking a snapshot of a virtual machine with memory, you may experience these symptoms while the memory is being written to disk:
- The virtual machine becomes unresponsive or inactive.
- The virtual machine does not respond to any commands.
- You cannot ping the virtual machine.
Environment
VMware vSphere ESXi 6.0
VMware vSphere ESXi 6.7
VMware vSphere ESXi 6.5
VMware vSphere ESXi 7.0.0
VMware vSphere ESXi 6.7
VMware vSphere ESXi 6.5
VMware vSphere ESXi 7.0.0
Resolution
This is an expected behavior in ESXi. For more information, see Snapshots Take a Long Time When “Keep Memory” is Enabled (76687).
While taking a virtual machine snapshot with memory, the VM may appear to be unresponsive and the snapshot may take a long time to complete. This is because the ESXi host must dump the VM’s memory to disk.
In the vmware.log file, you will notice that during the snapshot creation, a feature called Lazy CheckPointing is utilized.
Lazy CheckPointing is a feature that allows the VM to continue running while the memory is dumped. It would otherwise have to stop the VM and dump the complete contents of the memory to disk. Instead of completely disrupting operations on the VM, the ESXi host can leave the VM running with degraded performance.
This Lazy CheckPointing mechanism takes a significant amount of time, and as a result, you experience degraded VM performance for a prolonged period.
Note: Time taken for this operation differs with the amount of memory assigned to the VM. For more information, see the Allocate Memory Resources section of the vSphere Virtual Machine Administration Guide.
For example:
If you take a snapshot of a virtual machine with 4 GB of RAM, you see similar entries in the vmware.log file:
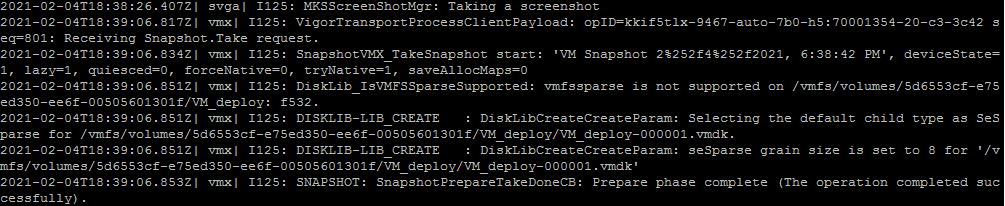
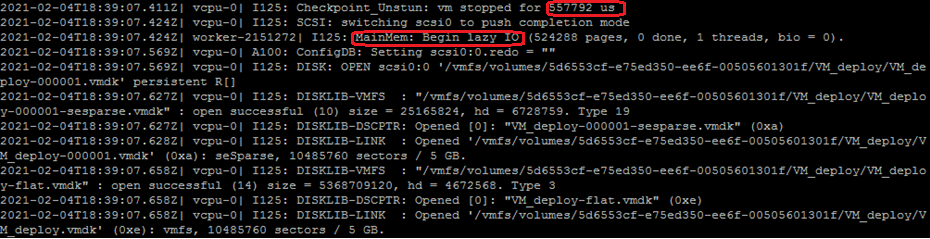
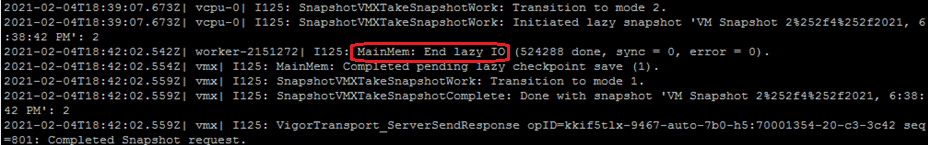
Note: The above example is only for reference, the time taken for the task in this example is on the basis of the environment and resources.
During the snapshot process, the virtual machine goes through the Fast Suspend Resume (FSR) process and the guest operating system is unresponsive. The time taken by a virtual machine in the FSR state is dependent on the memory to be written to disk for such an operation, and the speed and responsiveness of the datastore's backing storage.
When the memory is completely written on the disk, the virtual machine resumes normal operation.
While taking a virtual machine snapshot with memory, the VM may appear to be unresponsive and the snapshot may take a long time to complete. This is because the ESXi host must dump the VM’s memory to disk.
In the vmware.log file, you will notice that during the snapshot creation, a feature called Lazy CheckPointing is utilized.
Lazy CheckPointing is a feature that allows the VM to continue running while the memory is dumped. It would otherwise have to stop the VM and dump the complete contents of the memory to disk. Instead of completely disrupting operations on the VM, the ESXi host can leave the VM running with degraded performance.
This Lazy CheckPointing mechanism takes a significant amount of time, and as a result, you experience degraded VM performance for a prolonged period.
Note: Time taken for this operation differs with the amount of memory assigned to the VM. For more information, see the Allocate Memory Resources section of the vSphere Virtual Machine Administration Guide.
For example:
If you take a snapshot of a virtual machine with 4 GB of RAM, you see similar entries in the vmware.log file:
Note: The above example is only for reference, the time taken for the task in this example is on the basis of the environment and resources.
During the snapshot process, the virtual machine goes through the Fast Suspend Resume (FSR) process and the guest operating system is unresponsive. The time taken by a virtual machine in the FSR state is dependent on the memory to be written to disk for such an operation, and the speed and responsiveness of the datastore's backing storage.
When the memory is completely written on the disk, the virtual machine resumes normal operation.
Feedback
Yes
No
